Fluid and electrolyte case studies for nursing students present a unique opportunity to delve into the intricacies of fluid and electrolyte management, equipping nurses with the knowledge and skills to provide optimal patient care. This comprehensive guide explores the different types of fluid and electrolyte imbalances, their signs and symptoms, and evidence-based nursing interventions for effective management.
Through engaging case studies, nurses will gain practical insights into the assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation of care for patients with fluid and electrolyte imbalances. By integrating the principles of fluid and electrolyte management, nurses can confidently navigate complex clinical scenarios and ensure positive patient outcomes.
Fluid Imbalances: Fluid And Electrolyte Case Studies For Nursing Students
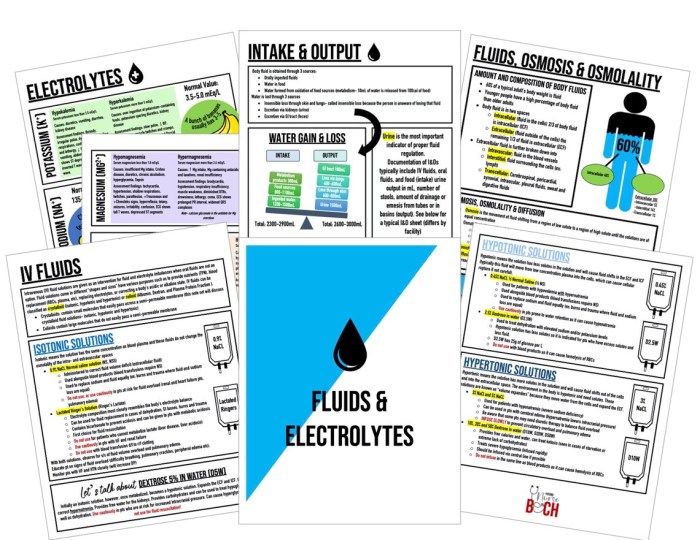
Fluid imbalances occur when the body’s fluid volume is either too low (dehydration) or too high (overhydration). Dehydration results from a loss of fluids, such as through sweating, vomiting, or diarrhea. Overhydration, on the other hand, occurs when the body retains too much fluid.
Signs and Symptoms of Fluid Imbalances
- Dehydration: Dry mouth, thirst, sunken eyes, rapid pulse, low blood pressure, decreased urine output, fatigue
- Overhydration: Edema (swelling), weight gain, headache, nausea, vomiting, confusion
Nursing Interventions for Managing Fluid Imbalances
- Dehydration: Provide oral or intravenous fluids, monitor fluid intake and output, weigh the patient daily
- Overhydration: Restrict fluid intake, administer diuretics, monitor fluid intake and output, weigh the patient daily
Electrolyte Imbalances
Electrolyte imbalances occur when the levels of electrolytes (e.g., sodium, potassium, calcium) in the body are too high or too low. Electrolyte imbalances can be caused by various factors, such as dehydration, overhydration, kidney disease, and certain medications.
Signs and Symptoms of Electrolyte Imbalances
- Hyponatremia(low sodium): Confusion, fatigue, seizures, coma
- Hypernatremia(high sodium): Thirst, dry mouth, muscle cramps, seizures
- Hypokalemia(low potassium): Muscle weakness, fatigue, irregular heartbeat
- Hyperkalemia(high potassium): Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, muscle weakness, irregular heartbeat
Nursing Interventions for Managing Electrolyte Imbalances, Fluid and electrolyte case studies for nursing students
- Hyponatremia: Administer hypertonic saline, monitor sodium levels, restrict fluid intake
- Hypernatremia: Administer hypotonic fluids, monitor sodium levels, provide oral or intravenous fluids
- Hypokalemia: Administer potassium supplements, monitor potassium levels, provide oral or intravenous fluids
- Hyperkalemia: Administer calcium gluconate, monitor potassium levels, restrict potassium intake
Fluid and Electrolyte Management
Fluid and electrolyte management is crucial for maintaining homeostasis in the body. The principles of fluid and electrolyte management include assessing the patient’s fluid and electrolyte status, determining the appropriate type and amount of fluids and electrolytes to administer, and monitoring the patient’s response to treatment.
Methods of Fluid and Electrolyte Administration
- Oral: Fluids and electrolytes can be administered orally in the form of water, juice, or electrolyte-containing drinks.
- Intravenous: Fluids and electrolytes can be administered intravenously through a peripheral or central line.
- Enteral: Fluids and electrolytes can be administered enterally through a nasogastric or gastrostomy tube.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: A 65-year-old male presents to the emergency department with symptoms of dehydration, including dry mouth, thirst, and sunken eyes. The patient has been experiencing diarrhea for the past 2 days.
Nursing Assessment: The nurse assesses the patient’s fluid status, vital signs, and weight. The nurse also obtains a history of the patient’s symptoms and medication use.
Nursing Diagnosis: Dehydration related to diarrhea
Nursing Planning: The nurse develops a plan of care to address the patient’s dehydration, including providing oral or intravenous fluids, monitoring fluid intake and output, and weighing the patient daily.
Nursing Implementation: The nurse provides the patient with oral fluids and monitors the patient’s fluid intake and output. The nurse also weighs the patient daily to track progress.
Nursing Evaluation: The nurse evaluates the patient’s response to treatment by monitoring the patient’s symptoms, vital signs, and weight. The nurse also monitors the patient’s fluid intake and output to ensure that the patient is adequately hydrated.
Case Study 2: A 72-year-old female presents to the emergency department with symptoms of overhydration, including edema, weight gain, and headache. The patient has been taking a diuretic for the past 6 months.
Nursing Assessment: The nurse assesses the patient’s fluid status, vital signs, and weight. The nurse also obtains a history of the patient’s symptoms and medication use.
Nursing Diagnosis: Overhydration related to diuretic use
Nursing Planning: The nurse develops a plan of care to address the patient’s overhydration, including restricting fluid intake, administering diuretics, monitoring fluid intake and output, and weighing the patient daily.
Nursing Implementation: The nurse restricts the patient’s fluid intake and administers diuretics as prescribed. The nurse also monitors the patient’s fluid intake and output and weighs the patient daily to track progress.
Nursing Evaluation: The nurse evaluates the patient’s response to treatment by monitoring the patient’s symptoms, vital signs, and weight. The nurse also monitors the patient’s fluid intake and output to ensure that the patient is no longer overhydrated.
Query Resolution
What are the different types of fluid imbalances?
Fluid imbalances can be classified as dehydration (hypovolemia) or overhydration (hypervolemia).
What are the signs and symptoms of hyponatremia?
Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include nausea, vomiting, confusion, seizures, and coma.
How are fluid and electrolytes administered?
Fluid and electrolytes can be administered orally, intravenously, or through other routes as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
