Nursing diagnosis for hip arthroplasty is a critical aspect of providing comprehensive care to patients undergoing this surgical procedure. This article delves into the concept of nursing diagnosis, common diagnoses related to hip arthroplasty, and the essential role of nurses in assessing, intervening, and educating patients throughout their recovery journey.
Hip arthroplasty, commonly known as hip replacement surgery, aims to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and restore function in individuals with severe hip joint damage. Nurses play a pivotal role in optimizing patient outcomes by identifying and addressing potential complications, promoting self-care, and ensuring a smooth transition back to daily life.
Overview of Hip Arthroplasty

Hip arthroplasty, also known as hip replacement surgery, is a surgical procedure to replace the damaged or diseased hip joint with an artificial joint. It is a common orthopedic procedure performed to relieve pain, improve mobility, and restore function in patients with severe hip arthritis or other hip conditions.
There are two main types of hip arthroplasty procedures: total hip arthroplasty (THA) and partial hip arthroplasty (PHA). THA involves replacing both the ball (femoral head) and socket (acetabulum) of the hip joint, while PHA replaces only the damaged ball of the hip joint.
Nursing Diagnosis for Hip Arthroplasty

Nursing diagnosis is a clinical judgment about an individual, family, or community response to actual or potential health conditions/life processes. It provides the basis for selecting nursing interventions to achieve outcomes for which the nurse is accountable.
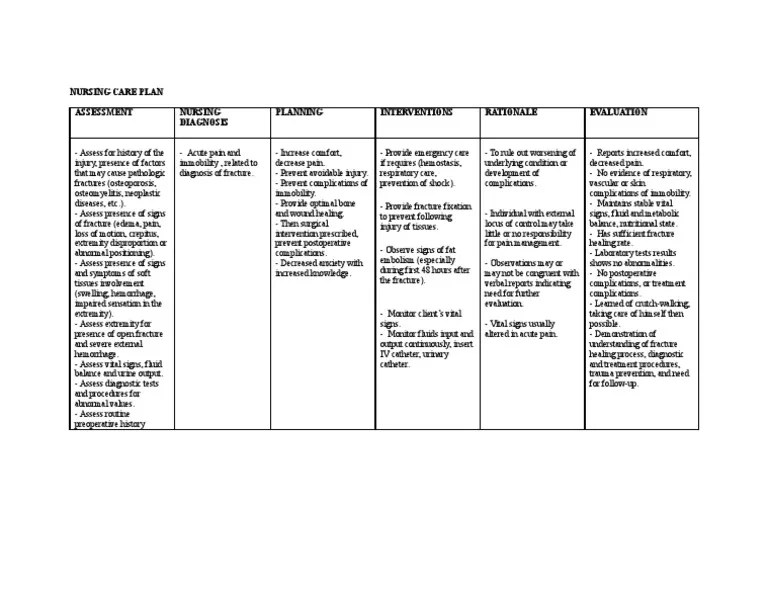
Common nursing diagnoses related to hip arthroplasty include:
- Acute pain related to surgical incision and inflammation
- Impaired physical mobility related to pain and joint stiffness
- Risk for infection related to surgical wound
- Deficient knowledge related to postoperative care and activity restrictions
- Self-care deficit related to impaired mobility
Assessment of Patients Undergoing Hip Arthroplasty
Nurses play a crucial role in assessing patients before and after hip arthroplasty. Preoperative assessment includes evaluating the patient’s pain level, mobility, functional status, and overall health. Postoperative assessment focuses on monitoring the patient’s recovery, including pain management, wound healing, and functional progress.
Nursing Interventions for Hip Arthroplasty
Nursing interventions for hip arthroplasty aim to address the identified nursing diagnoses and promote the patient’s recovery. These interventions include:
- Administering pain medication as prescribed
- Assisting with mobility and range of motion exercises
- Monitoring for signs of infection
- Educating the patient on postoperative care and activity restrictions
- Assisting with activities of daily living as needed
Patient Education and Discharge Planning
Patient education and discharge planning are essential components of nursing care for hip arthroplasty patients. Nurses provide instructions on pain management, wound care, and activity restrictions. They also discuss the importance of physical therapy and follow-up appointments.
Collaboration with Other Healthcare Professionals
Interdisciplinary collaboration is crucial in hip arthroplasty care. Nurses work closely with surgeons, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and other healthcare professionals to ensure the patient’s needs are met throughout the perioperative period.
Research and Evidence-Based Practice: Nursing Diagnosis For Hip Arthroplasty
Evidence-based practice is essential in nursing care for hip arthroplasty patients. Nurses stay updated on the latest research findings and incorporate them into their practice to provide the best possible care.
Clarifying Questions
What are the most common nursing diagnoses related to hip arthroplasty?
Common nursing diagnoses include pain, impaired physical mobility, risk for infection, and risk for falls.
How do nurses assess patients before and after hip arthroplasty?
Nurses assess patients’ pain levels, mobility, functional status, wound healing, and overall well-being.
What are some examples of nursing interventions for patients undergoing hip arthroplasty?
Nursing interventions may include pain management, wound care, mobility assistance, and patient education on pain management, activity restrictions, and lifestyle modifications.