Littoral rights vs riparian rights – Littoral rights and riparian rights are two distinct legal doctrines that govern the use and ownership of waterfronts. This article delves into the intricacies of these rights, exploring their definitions, characteristics, similarities, differences, legal frameworks, and practical implications.
Littoral rights are associated with tidal waters, while riparian rights apply to non-tidal waters. Both types of rights grant certain privileges to landowners adjacent to water bodies, but they also impose specific responsibilities and limitations.
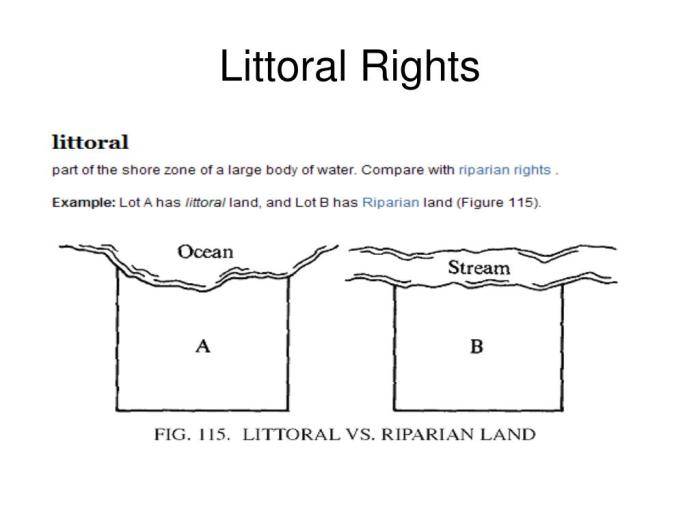
Definition of Littoral Rights

Littoral rights refer to the legal rights and privileges granted to owners of property adjacent to a body of water, such as a sea, lake, or river. These rights are primarily concerned with the use and enjoyment of the water and the land adjacent to it.
The scope of littoral rights varies depending on the jurisdiction and the specific body of water involved. However, common littoral rights typically include the right to access the water, navigate and fish, build structures such as docks and piers, and enjoy the scenic and recreational benefits of the water.
Definition of Riparian Rights
Riparian rights are similar to littoral rights but apply specifically to property owners whose land borders a river or stream. These rights are based on the principle that riparian owners have a right to use and enjoy the water that flows past their property.
The scope of riparian rights also varies depending on the jurisdiction and the specific watercourse involved. However, common riparian rights typically include the right to access the water, withdraw water for domestic and agricultural purposes, generate hydroelectric power, and enjoy the scenic and recreational benefits of the water.
Similarities and Differences between Littoral Rights and Riparian Rights: Littoral Rights Vs Riparian Rights
Commonalities
- Both littoral rights and riparian rights are based on the principle that property owners have a right to use and enjoy the water adjacent to their land.
- Both types of rights include the right to access the water, navigate, and fish.
- Both littoral and riparian rights are subject to regulation by government agencies to protect the public interest and the environment.
Differences, Littoral rights vs riparian rights
- Littoral rights apply to property owners adjacent to large bodies of water, such as seas and lakes, while riparian rights apply to property owners adjacent to rivers and streams.
- Littoral rights typically include the right to build structures on the water, such as docks and piers, while riparian rights do not.
- Riparian rights typically include the right to withdraw water for domestic and agricultural purposes, while littoral rights do not.
Common Queries
What are the key differences between littoral rights and riparian rights?
Littoral rights are associated with tidal waters, while riparian rights apply to non-tidal waters. Littoral rights typically include the right to access the water, construct docks or piers, and engage in certain recreational activities. Riparian rights, on the other hand, focus on the use of water for domestic, agricultural, and industrial purposes.
How are littoral and riparian rights acquired?
Littoral rights are generally acquired through ownership of land adjacent to tidal waters. Riparian rights are acquired through ownership of land adjacent to non-tidal waters.
What are the legal frameworks governing littoral and riparian rights?
Littoral and riparian rights are governed by a combination of common law principles and statutory regulations. The specific legal frameworks vary depending on the jurisdiction.