Helical gear left or right – Helical gears, with their distinctive slanted teeth, introduce a fascinating chapter in the realm of mechanical engineering. As we delve into the intricacies of helical gears, we’ll explore the differences between right-hand and left-hand variations, unravel their applications, and uncover the secrets behind their manufacturing and design.
The unique properties of helical gears make them indispensable in a wide range of industries, from automotive to aerospace. By understanding the nuances of these gears, engineers and technicians can harness their power to create innovative and efficient solutions.
Helical Gear Terminology
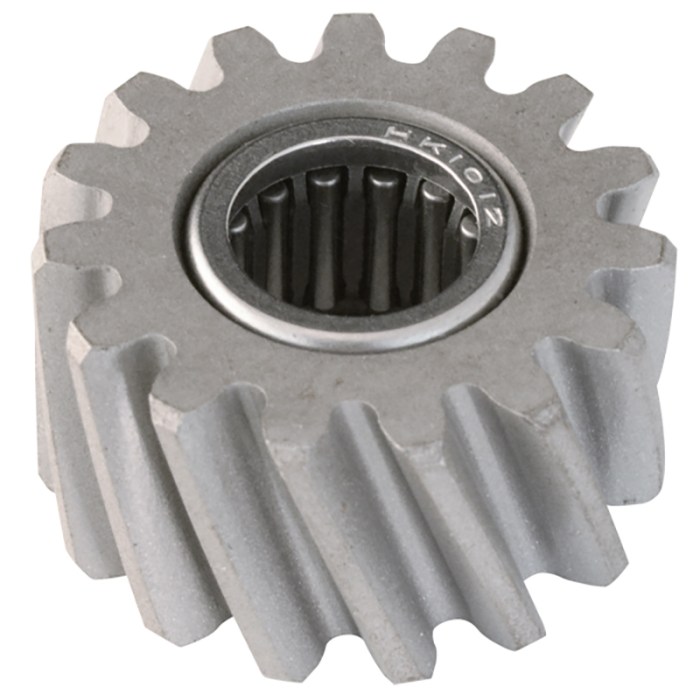

Helical gears are a type of gear that has teeth that are cut at an angle to the face of the gear. This design allows for smoother and quieter operation than spur gears, which have teeth that are cut straight across the face of the gear.
Right-Hand and Left-Hand Helical Gears, Helical gear left or right
Helical gears can be either right-hand or left-hand. The direction of the helix (the angle of the teeth) determines whether the gear is right-hand or left-hand. In a right-hand helical gear, the helix is angled to the right when viewed from the front of the gear.
Helical gears can be either left or right-handed, and it’s important to determine the correct type for your application. If you’re not sure which type you need, you can consult a resource like hrk physics volume 1 pdf for guidance.
Once you know the correct type of helical gear, you can ensure that it operates efficiently and effectively in your system.
In a left-hand helical gear, the helix is angled to the left when viewed from the front of the gear.
Applications of Right-Hand and Left-Hand Helical Gears
Right-hand helical gears are typically used in applications where the gears need to rotate in the same direction. This is because the helix of a right-hand helical gear causes the gears to push each other apart as they rotate, which helps to prevent them from binding.
Left-hand helical gears are typically used in applications where the gears need to rotate in opposite directions. This is because the helix of a left-hand helical gear causes the gears to pull each other together as they rotate, which helps to keep them from separating.
Manufacturing Helical Gears
The manufacturing process of helical gears involves several key steps to ensure precision and durability.
Initially, the gear blank is cut from a solid piece of metal, typically steel or alloy steel. The blank is then shaped using a hobbing machine, which employs a rotating cutting tool called a hob to create the helical teeth.
The hobbing process generates the desired tooth profile and helix angle.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment plays a crucial role in enhancing the strength and durability of helical gears. After hobbing, the gears undergo a series of heat treatment processes, including hardening and tempering.
Hardening involves heating the gear to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it, which increases the hardness of the teeth. Tempering follows the hardening process, where the gear is reheated to a lower temperature and cooled slowly. This process reduces the brittleness caused by hardening, resulting in a more resilient gear.
Design Considerations for Helical Gears

Designing helical gears involves considering various factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity. These factors include:
- Load capacity:Determine the maximum load that the gears can handle without excessive wear or failure.
- Speed:Consider the operating speed of the gears and ensure they are designed to withstand the associated centrifugal forces.
- Noise:Helical gears are generally quieter than spur gears, but noise levels can vary depending on factors such as tooth profile and helix angle.
- Efficiency:The helix angle influences the efficiency of helical gears, with higher helix angles resulting in lower sliding friction and higher efficiency.
Selecting the Appropriate Helical Gear
When selecting helical gears for a specific application, consider the following guidelines:
- Load capacity:Choose gears with a load capacity that exceeds the expected load to ensure durability.
- Speed:Select gears with an appropriate helix angle to minimize noise and maximize efficiency at the operating speed.
- Material:Consider the operating environment and load requirements to determine the appropriate material for the gears.
- Lubrication:Ensure the gears are properly lubricated to reduce wear and extend their lifespan.
Importance of Backlash in Helical Gear Design
Backlash, the amount of play between mating gear teeth, is an important factor in helical gear design. Proper backlash ensures:
- Smooth operation:Backlash allows for minor misalignments and prevents binding.
- Reduced noise:Adequate backlash minimizes tooth impact and reduces noise.
- Increased efficiency:Backlash allows for a small amount of sliding motion, which can improve efficiency.
Excessive backlash, however, can lead to increased vibration and premature wear. Therefore, it is crucial to determine the optimal backlash for the specific application.
Applications of Helical Gears

Helical gears find widespread use across various industries due to their unique characteristics and advantages. They are particularly suitable for applications requiring smooth and quiet operation, high power transmission, and efficient speed reduction.
Industrial Applications
- Automotive Industry:Helical gears are commonly used in transmissions, differentials, and other powertrain components to achieve smooth and efficient power transfer.
- Heavy Machinery:In industries such as mining, construction, and manufacturing, helical gears are employed in gearboxes, conveyors, and other heavy-duty machinery.
- Aerospace:Helical gears are used in aircraft engines, gearboxes, and landing gear systems due to their high load-bearing capacity and ability to withstand extreme conditions.
Advantages of Helical Gears
- Smooth and Quiet Operation:The helical teeth design ensures a gradual engagement, resulting in less noise and vibration compared to spur gears.
- High Power Transmission:Helical gears can transmit higher power than spur gears due to their increased contact area and longer tooth engagement.
- Efficient Speed Reduction:Helical gears are suitable for applications requiring high speed reduction ratios, as their helical teeth allow for a more gradual change in speed.
Disadvantages of Helical Gears
- Axial Thrust:Helical gears generate an axial thrust force due to the angled teeth, which must be accounted for in the design and supported by bearings.
- Manufacturing Complexity:Helical gears are more complex to manufacture compared to spur gears, requiring specialized cutting tools and higher precision.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Helical Gears

Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of helical gears. Regular inspections, lubrication, and adjustments help prevent premature wear, extend the gear’s lifespan, and minimize downtime.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
- Excessive Noise:This can indicate misalignment, worn bearings, or improper lubrication.
- Vibration:Can be caused by imbalance, loose gears, or shaft misalignment.
- Heat Buildup:Excessive friction due to improper lubrication, overloading, or misalignment.
- Tooth Wear:Premature wear can be caused by poor lubrication, overloading, or abrasive particles in the lubricant.
Signs of Wear and Tear
- Pitting:Small indentations on the gear teeth, caused by repeated contact under heavy loads.
- Spalling:Flaking or chipping of the gear teeth, indicating fatigue or excessive stress.
- Scoring:Grooves or scratches on the gear teeth, resulting from abrasive wear or poor lubrication.
- Tooth Flank Wear:Gradual wear of the tooth flanks, leading to reduced tooth contact and increased noise.
FAQ Overview: Helical Gear Left Or Right
What is the primary distinction between right-hand and left-hand helical gears?
The direction of the tooth helix determines the handedness of helical gears. Right-hand gears have teeth that spiral clockwise when viewed from the gear’s end, while left-hand gears have teeth that spiral counterclockwise.
How are helical gears manufactured?
Helical gears are typically manufactured using a hobbing process, where a rotating cutting tool called a hob gradually shapes the gear teeth. Other methods include shaping, milling, and grinding.
What is the significance of backlash in helical gear design?
Backlash refers to the amount of play between mating helical gears. Proper backlash adjustment is crucial to prevent excessive wear and noise while ensuring smooth gear operation.