Baby Boom AP Human Geography delves into the historical, demographic, economic, social, and cultural impact of the baby boom generation in the United States. This comprehensive analysis explores the factors contributing to the surge in birth rates, the unique characteristics of the baby boom generation, and the challenges and opportunities presented by their aging.
As we delve deeper, we’ll examine the economic impact of the baby boom on the U.S. economy, their role in the growth of suburbs and the consumer economy, and the potential economic challenges posed by their retirement. Additionally, we’ll explore the social and cultural changes that occurred during the baby boom era, their influence on popular culture, education, and politics, and the lasting legacy they’ve left on American society.
Historical Context
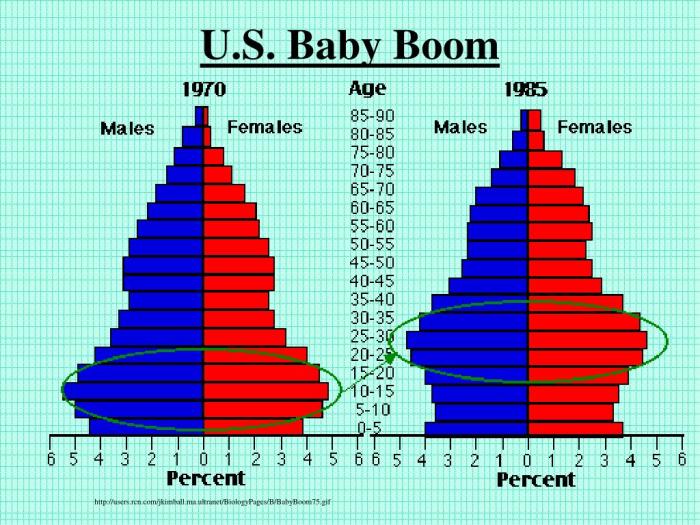
The baby boom in the United States was a period of unusually high birth rates that occurred between 1946 and 1964. During this time, the birth rate in the US reached its highest level in history, with over 4 million babies born in each of those years.
The baby boom was caused by a number of factors, including the end of World War II, which led to a surge in marriages and births. Other factors that contributed to the baby boom included the availability of affordable housing and the growth of the suburbs, which made it easier for families to have children.
Baby boom AP Human Geography students may be interested in exploring the story of reality as told by Greg Koukl. Understanding the concept of reality can help students better grasp the social and environmental challenges facing our world today. By examining the story of reality, students can gain valuable insights into the factors that shape human behavior and the complexities of global issues, enriching their understanding of AP Human Geography.
Social and Economic Implications
The baby boom had a profound impact on American society. The large number of children born during this period led to a strain on schools, hospitals, and other public services. The baby boom also contributed to the growth of the suburbs and the rise of the consumer economy.
Demographic Characteristics
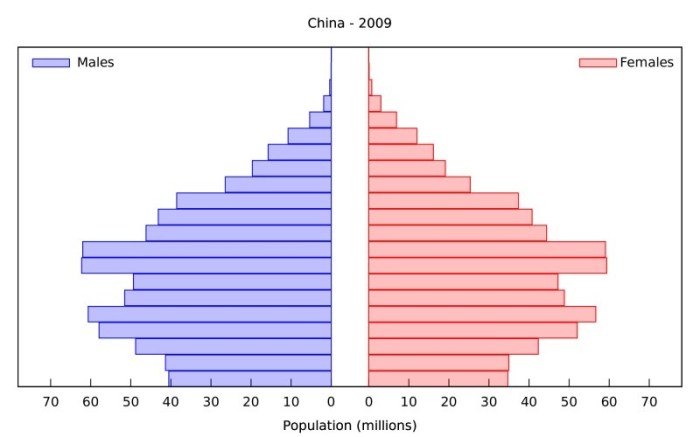
The baby boom generation, born between 1946 and 1964, is characterized by its unprecedented size and growth rate. This generation has significantly shaped the United States’ population age structure and presents both challenges and opportunities for society.
Age Structure
The baby boom generation has created a “bulge” in the age distribution of the US population, with a large proportion of individuals in their 50s and 60s. This age bulge is expected to continue moving through the age pyramid as the baby boomers age.
Challenges
As the baby boom generation ages, it will face challenges related to healthcare, retirement, and social security. The increasing number of elderly individuals may strain healthcare systems and increase demand for long-term care services. Additionally, the retirement of baby boomers will reduce the size of the workforce, potentially affecting economic growth and productivity.
Opportunities
The aging baby boom generation also presents opportunities. Their accumulated knowledge, experience, and financial resources can be valuable assets to society. Additionally, the increasing number of retirees can create new markets for products and services tailored to their needs.
Economic Impact
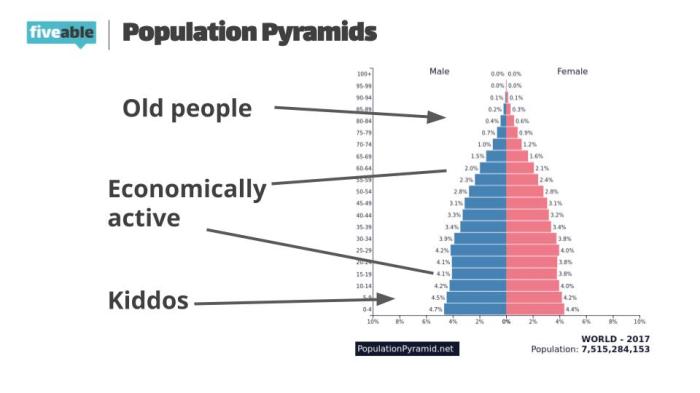
The baby boom generation, born between 1946 and 1964, had a profound impact on the U.S. economy. As this large cohort entered the workforce, they fueled economic growth and helped shape the consumer economy. However, the retirement of the baby boomers poses potential economic challenges.
Role in Economic Growth
The baby boomers entered the workforce in the 1960s and 1970s, a time of rapid economic growth. Their large numbers helped to increase the labor force and boost productivity. They also fueled the growth of the suburbs and the consumer economy.
As they purchased homes, cars, and other goods, they helped to create jobs and drive economic growth.
Growth of Suburbs and Consumer Economy
The baby boomers were the first generation to grow up in the suburbs. They were also the first generation to have a large disposable income. This combination led to the growth of the suburbs and the consumer economy. As the baby boomers moved to the suburbs, they created a demand for new homes, schools, and other infrastructure.
They also spent their disposable income on cars, appliances, and other consumer goods.
Challenges of Retirement, Baby boom ap human geography
The baby boomers are now beginning to retire. This will have a significant impact on the U.S. economy. As they leave the workforce, the labor force will shrink, which could lead to a slowdown in economic growth. Additionally, the retirement of the baby boomers will put a strain on Social Security and Medicare.
These programs are already facing financial challenges, and the retirement of the baby boomers will only make the situation worse.
Social and Cultural Impact: Baby Boom Ap Human Geography
The baby boom generation, born between 1946 and 1964, left an enduring imprint on American society. Their sheer numbers and distinctive values reshaped various aspects of social and cultural life.
During the baby boom era, a youth culture emerged, characterized by a rejection of traditional norms and a embrace of individuality and experimentation. This cultural shift was reflected in popular music, fashion, and literature, with rock and roll becoming the soundtrack of a generation and the rise of counterculture movements.
Education
The baby boom also had a significant impact on education. The influx of students strained existing school systems, leading to the construction of new schools and the expansion of higher education. The baby boomers’ demand for accessible and relevant education contributed to the growth of community colleges and the establishment of new universities.
Politics
The baby boom generation also played a pivotal role in shaping American politics. Coming of age during the Vietnam War and the civil rights movement, they brought a spirit of activism and a desire for social change to the political arena.
Their involvement in protest movements and the anti-war effort had a lasting impact on American politics.
Legacy
The baby boom generation has left a lasting legacy on American society. Their values, such as individualism, self-expression, and a focus on personal fulfillment, continue to shape American culture. The social and cultural changes they initiated have had a profound impact on subsequent generations, and their influence is still felt today.
Query Resolution
What were the key factors contributing to the baby boom?
The post-World War II economic prosperity, increased access to healthcare, and changing social norms played significant roles.
How has the baby boom generation influenced the age structure of the U.S. population?
The baby boom generation is the largest generation in U.S. history, creating a bulge in the age pyramid.
What are the potential economic challenges posed by the retirement of the baby boom generation?
The retirement of the baby boom generation could strain social security and healthcare systems and reduce the size of the workforce.